Brown Invents
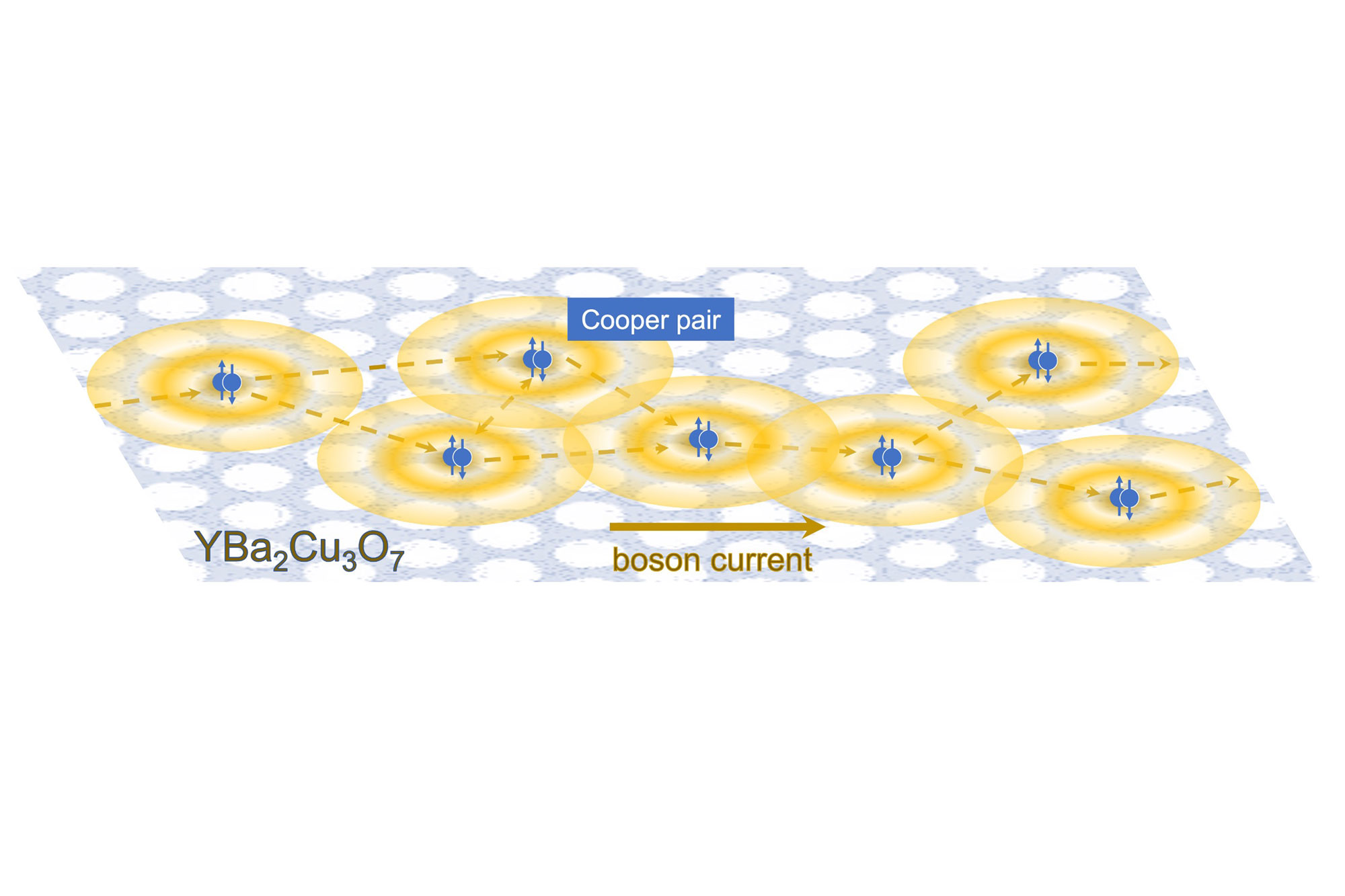
Strange metals, discovered around 30 years ago, are materials related to high-temperature superconductors and share fundamental quantum attributes with black holes. High-temperature superconductors conduct electricity with zero resistance at temperatures far above normal superconductors. The two fundamental classes of subatomic particles are fermions and bosons, which usually behave very differently. However, a research team co-led by Brown physics professor James Valles has found strange metal behavior in a material in which electrical charge is carried not by electrons, which are fermions, but by more wavelike entities called Cooper pairs. Although they consist of two electrons, Cooper pairs are bosons. Using a material called yttrium barium copper oxide, Valles and his team discovered strange metal behavior in a Cooper-pair metallic state—the first time strange metal behavior had been seen in a bosonic system. The findings, reported in Nature in January 2022, could help scientists understand strange metal behavior, such as high-temperature superconductivity, and potentially provide fundamental insights into the quantum world.
